The 'Etc' menu's command 'Options' allows you to adjust a number of MRIcro's settings. First of all, you can select which slices will appear when the 'multislice' button is pressed. There are twelve data fields, allowing up to twelve slices to be viewed simultaneously. Fields that are set to zero will not be presented, allowing you to show fewer than twelve slices. You can also select whether the multislice button will generate coronal or transverse images. The 'defaults' button at the bottom of the window will select a common set of slices useful for viewing images that have been normalised to SPM's T1 template.
The 'include sagittal' check box selects whether or not a sagittal view will appear when the 'multislice' button is pressed. The option window also includes a number of additional check boxes that describe how the multislice view will be presented. A few of the less intuitive options are shown in the figures below. Once you have selected the desired options, you can press 'OK' to save your selection, or 'Cancel' to ignore your changes.
A number of these options are described in the tutorial, and some are illustrated in the figures below. If there is no atom, or if imol is not a valid model molecule, return False. If there is no atom, or if imol is not a valid model molecule, return scheme false. "Rotate/Translate Zone" from the "Model/Fit/Refine" menu allows manual movement of a zone. The atoms selected in the moving fragment have the same alternate conformation code as the first atom you click.
To actuate a transformation, click and drag horizontally across the relevant button in the newly-created "Rotation & Translation" dialog. The axis system of the rotations and translations are the screen coordinates. Alternatively 59, you can click using left-mouse on an atom in the fragment and drag the fragment around. Use Control Left-mouse to move just one atom, rather than the whole fragment. If you click Control Left-mouse whilst not over an atom then you can rotate the fragment using mouse drag. MRIcro uses a palette of 256 colours for drawing brain images.
Because Windows reserves a number of colours, your display should be set to a 16-bit 24-bit or 32-bit colour palette. If your computer can not support more than 256 colours, you should switch off the 'graphics acceleration' check box in the options window (select 'options' from the Etc menu). To find out the current setting, open the 'display ' control panel and select the 'settings' tab. Using a colour palette of less than 16 bits (e.g. 256 colours) will limit the levels of gray that MRIcro can display.
Fewer gray levels are used when viewing multiple regions of interest. As with finding ligands, you are given a choice of maps, protein atoms. A final selection has to be made for the cut-off level, note that this value is the number of standard deviation of the density of the map before the map has been masked. The default sigma level is set for a "2Fo-Fc"-style map. If you want to use a difference map, you must change the sigma level otherwise you run the risk of fitting waters to difference map noise peaks. Return a list of (list imol chain-id resno ins-code atom-name alt-conf) for atom that is closest to the screen centre in any displayed molecule.
If there are multiple models with the same coordinates at the screen centre, return the attributes of the atom in the highest number molecule number. When you have selected the desired clipping and check box options, press one of the three file save buttons that are located at the bottom of the window. The buttons 'Save ' and 'Save ' will save the files as Analyze format images. SPMwin, SPM99, SPM2 and MRIcro can all read either big or little-endian Analyze files, while SPM96 requires the images to be in the same format as the machine used. The 'Save Dicom' button will save the image as a DICOM format image .
Note that the DICOM format image will either be in 8-bit integer or 16-bit integer format irregardless of the data type seleted. You can adjust the contrast for a specific region by dragging over the area of the image while depressing the RIGHT mouse button. The brightness and contrast values are adjusted to scale the selected area. Note that this will not work if you have selected any of the region-of-interest drawing tools .
This histogram shows the image intensity profile for the image 'IconT1'. Histograms can also be created for user defined regions of interest . Note the Threshold Mn value is listed, this can be used to set the image intensity scale of a target image to match an SPM template . The histogram button (located at the bottom-left of the panel) displays the voxel brightness distribution in the currently open image . When viewing axial, sagittal or coronal views, a slider appears that allows you to set which slice is displayed .
When projection views are displayed, you can set the X, Y and Z coordinates independently by adjusting the three edit boxes. The brightness and control the contrast of the image by changing the values located next to the sun and contrast images. These numbers describe the window center and window width of the display. The window centre refers to the image intensity that will be displayed as a medium-gray and the window width describes the range between bright white and full black.
Clicking the 'auto contrast' button sets 1% of the image to be maximum black and 1% to be maximum white. The autobalance works well for MRI scans, but often is not appropriate for CT scans, where the bones appear much brighter than the background and brain tissue. For CT scans, you can often get good settings by choosing one of the 'Contrast Preset ' in the 'View' window. For example, the 'Bone' preset sets the window center to be 400 and the width to 2000, and is often useful for highlighting bone in CT scans.
Each ligand is fitted with rigid body refinement to each potential ligand site in the map and the best one for each site selected and written out as a pdb file. The clusters are sorted by size, the biggest one first . The output placed ligands files have a prefix "best-overall" and are tagged by the cluster index and residue type of the best fit ligand in that site.
A component used to search for records and files when only limited information is known. Quick Search can be used to search the knowledge base no matter what navigation list is displayed or what is open on the content pane. Oracle Service Cloud contains a number of default Quick Search reports, and other reports can be added to the Quick Search button in navigation sets. The area on the left and right side of the console where staff members work with navigation lists, select items to open on the content pane, and search the knowledge base. In the default configuration, the left navigation pane contains Recent Items and Navigation tool windows; the right navigation pane contains the Quick Search tool window.
What appears on the navigation pane depends on the navigation set assigned in each staff member's profile and the permissions assigned in the profile. Each navigation pane can also be customized by staff members. See also Configuration button, navigation buttons, and Tool window.
The application menu also contains options for changing personal settings and password and customizing the content pane and navigation pane display. Staff members can also exit their application from this menu. The ROI menu's 'Export Image as ROI' converts an Analyze format image in MRIcro's custom ROI format. Note that the ROI format is binary -the ROI does not store intensity information. Load the image you wish to convert before selecting this command. When you select this item, a window appears that allows you to set the intensity ROI's threshold.
As you adjust the threshold, the image will will preview the portions of the image will be included in the ROI. When you are happy with the selection, press the 'Save as ROI' button to create the new ROI. Information consisting of a user ID and password that allows customers to access certain functions on the customer portal, such as the Account Overview page. Customers can create an account by clicking the Sign Up link or the Your Account tab on the customer portal. Customer accounts are also automatically created when a customer without an account submits a question, which adds a contact record to the knowledge base. When you convert medical images to Analyze format, you can select a series of 2D images that will be stacked and saved as a single unified 3D Analyze format file.
Selecting 'Convert foreign to Analyze' from the 'Import' menu will create a new window that allows you to describe your images. ECAT images can be converted selecting the 'Convert ECAT to Analyze' command from the import menu. ECAT images can be saved as the raw data or as scaled data - the conversion format can be selected in by choosing 'Etc/Options' and setting the 'ECAT convert' values. Finally, you can convert SPMwin headers to SPM headers using the 'Import/SPMwin VHD to Analyze' command.
Selecting the free rotate button causes a new window titled 'Free Rotate' to appear . This window allows you to select which oblique section you wish to view. You can independently set the yaw, roll, and pitch of the scan. Furthermore, you can select which slice you wish to view. The 'pivot' settings allow you to set the axis for the image rotations.
Note that the free rotate tools mix viewer centered and object centered coordinates, which can become somewhat disorienting. Also, when free rotating multiple Regions of interest with the 'interpolate' box checked, you may see a slight white halo around the regions. The Folder option can be used to attach a set of resources that are referenced as hyperlinks in your document, or as resources referenced in attached CSS or JavaScript files.
For example, perhaps you've created a custom navigational menu using additional CSS and JavaScript. Images needed for the menu can be put in a single folder and attached using the Folder field. This folder is moved to the assets/resources/ folder in the output. The paths to the images from CSS and JavaScript in the final output would then be ../assets/resources and the path from any attached HTML would be assets/resources/. Single atoms or residues can be deleted from the molecule using "Delete…" from the "Model/Fit/Refine"dialog.
Pressing this button results in a new dialog, with the options of "Residue" , "Atom" and "Hydrogen Atoms". Now click on an atom in the graphics - the deleted object will be the whole residue of the atom if "Residue" was selected and just that atom if "Atom" was selected. Note that if a residue has an alternative conformation, then "Delete Residue" will delete only the conformation that matches that alternative conformation specifier of the clicked atom. Use the "Run Refmac..." button to select the dataset and the coordinates on which you would like to run Refmac. Note that here Coot only allows the use of datasets which has Refmac parameters set as the MTZ file was read.
By default, Coot displays the new coordinates and the new map generated from refmac's output MTZ file. The "state"of Coot is saved on Exit and written to a file called 0-coot.state.scm 0-coot.state.py . An item added to a report that is used to return different data or data in different formats in the same column. For example, a single report can be created that displays the number of incidents by staff member, group, queue, or status. When running a report, the variable value is selected from the Search window or from docked filters. Report data that has been temporarily stored in the database for quicker report generation.
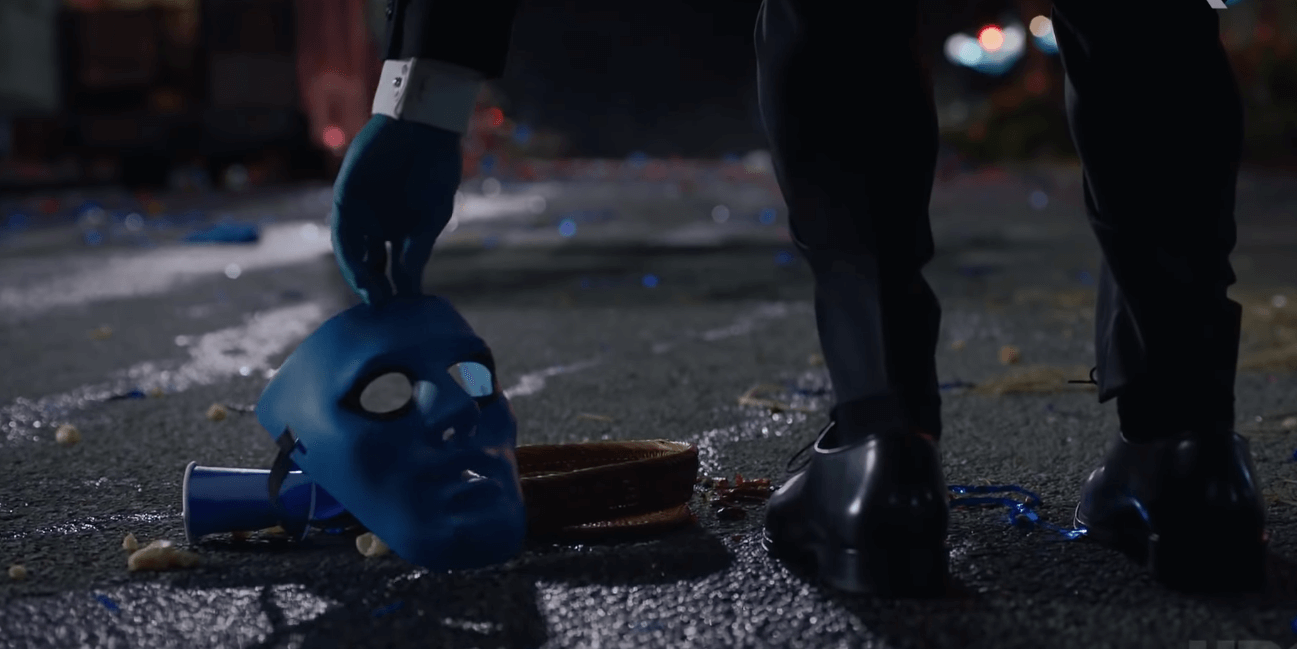
This data is cached nightly by the Agedatabaseutility and can be purged regularly. Cached data also refers to local cache files stored on a staff member's workstation. MRIcro automatically displays the amount of clipping selected, in this example the top five and bottom ten slices are about to be clipped. This figure also shows the 'Hot Metal' color lookup table. Before saving an image that you wish to rotate, you can check your settings by pressing the 'preview' button. The preview will show you two slices of how the image will appear after being rotated.
If your settings are correct, the preview should show two transverse slices . Make sure to check that the left/right mirroring is correct. Usually it is wise to save the data in the same format as the source image. Down-sampling an image (e.g. saving a 16-bit integer file as an 8-bit data file) will save disk space . Up-sampling an image (e.g. saving a 16-bit file as a 32-bit file) can be useful for when other programs require data of a specific type.
The clip top and clip bottom fields allow you to choose the number of slices that you want to shave off of the top or bottom of a scan . The 'Format' list box allows you to convert coronal or sagittal Analyze format images to axial format . Is 0, this will create a new map that has density only where there are no coordinates. Is 1 then the map density values will be set to zero everywhere except close to the atoms of molecule numberimol-model.
This creates a new residue at the C or N terminal extension of the residue clicked by fitting to the map. \phi,\psi angle pairs are selected at random based on the Ramachandran plot probability and fitted to the density. It is possible that a wrong position will be selected for the terminal residue and if so, you can reject this fit and try again with Fit Terminal Residue 84. Each of the trial positions are scored according to their fit to the map 85 and the best one selected. It is probably a good idea to run "Refine Zone" on these new residues.
Mutations are available on a 1-by-1 basis using the graphics. After selecting "Mutate…" from the "Model/Fit/Refine" dialog, click on an atom in the graphics. Select the new residue type you wish and the residue in the graphics is updated to the new residue type 77. The initial position of the new rotamer is the a priori most likely rotamer.
Note that in interactive mode, such as this, a residue type match 78 will not stop the mutation action occurring. By default, Auto Fit Rotamer will switch to "Backrub Rotamer"73mode when fitting against a map of worse than 2.7Å. This search mode moves the some atoms of the mainchain of the neighbouring residues.
The Ramachandran plot is not used in this fitting algorithm. There is a selector in the cif dictionary file chooser that allow you to select the molecule to which molecule refers. Each of the indididual molecules can be specifically selected. By default the non-auto-load list consists of INH, LIG, DRG, XXX, and the series LG0-9.
For both "Regularize Zone" and "Refine Zone" one is able to use a single click torefine a residue range. Pressing A on the keyboard while selecting an atom in a residue will automatically create a residue range with that residue in the middle. By default the zone is extended one residue either size of the central residue. This can be changed to 2 either side using (set-refine-auto-range-step 2). A collection of files that generates a specific function when it is placed on a page of the customer portal. An interface element for switching between the items currently open on the Service Console.